The articles presents the various aspects on Doing Business In Maharashtra India. Following points are covered in the article:
- Maharashtra – A favourite industrial destination and growth centre
- Ideal Industrial Infrastructure
- Industrial Regions and Groups
- Classification of Industrial Land (Free Hold and Lease Hold)
- Industrial Sectors
- SEZs in Maharashtra
- Check of Industrial Pollution
- Safety and Health
- Key approvals
- Industrial Policies
- Maharashtra – Perennial Leader in the Industry
The ‘Make in India’ campaign was launched to facilitate investment, foster innovation, enhance skill development, protect intellectual property & build best in class manufacturing infrastructure in 25 sectors of the economy by providing the high quality standards and minimizing the impact on the environment. The campaign proved to be the boom for the country, as India emerged the top destination globally for foreign direct investment (FDI), surpassing the United States as well as the People’s Republic of China. Keeping in line of the initiative, the Government of Maharashtra started the initiative ‘Make in Maharashtra’ creating business friendly atmosphere with the target in the addition of foreign direct investment (FDI) and local investment in the region. Regardless of the impact of demonetisation, Maharashtra government signed MoUs worth Rs. 3.65 Lakh Crores involved industrial projects, mainly in the field of manufacturing. The state’s latest data shows that investments worth Rs. 1.66 Lakh Crores from these MoUs with the industries department are “on track”. Doing Business In Maharashtra India is
Maharashtra is a state in the western region of India . India’s second-most populous state and third-largest state by area. It has a long coastline stretching nearly 720 Kms. along the Arabian Sea. Mumbai, the capital of Maharashtra and the financial capital of India, houses the headquarters of most of the major corporate & financial institutions. India’s main stock exchanges & capital market and commodity exchanges are located in Mumbai. Maharashtra is one of the biggest contributors to Indian economy; the state has been growing at a faster pace than all-India average in most periods and is expected to continue the momentum. The state contributes 27% of total exports in India. Being the biggest contributor to India’s GDP 15%, Maharashtra has always remained in the forefront of country’s economic development. In 2015, the state gross domestic GDP stood at 398 Billion Dollars. It contributes whopping 18.9 % of INDIA’S GDP. The state attracts the highest FDI in the country; ~ 30 percent of the total FDI inflow. According to the DIPP, cumulative FDI inflows in the state of Maharashtra during April 2000 to March 2016 stood US$ 82.62 Billion. The state government has approved 18,709 industrial proposals during 1991-92 to 2014-15.
Government of Maharashtra offers plethora of incentives to the Foreign companies for setting up their factories / manufacturing units in Maharashtra. To know in details as to how the foreign companies can make the investment in India to set up the industrial units and also the various incentives offered by the Government of Maharashtra please click here
MAHARASHTRA PROVIDES IDEAL INDUSTRIAL INFRASTRUCTURE
Maharashtra is the backbone of Indian economy. If India grows at 8 percent than astonishingly Maharashtra growth would be at least 10 percent as it is gravitational centre of the country. One of the factors that has made the state’s position so powerful is its strong infrastructure, an ideal destination for setting up of industries. Captive power plants, water supply, roads, waste management, drainage and effluent treatment at a very nominal rate is assured by the state government body resulting in multiple returns. It has 36 districts divided into six revenue divisions. Maharashtra’s infrastructure sector has grown significantly over the last decade, with a substantial rise in the number of industrial clusters and public-private partnership (PPP) projects.
The key highlights of the infrastructure are as under:-
Transportation: Industries in Maharashtra enjoy all the three modes of transportation i.e. Air, Surface and Water
- Three International and seven domestic airports.
- Two majors Ports (MBPT & JNPT) and 53 minor ports. Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust is the largest port in India in terms of container traffic.
- 18 national highways and 5,984 Kms. railway network.
- DMIC (Delhi – Mumbai Industrial Corridor) covering following states: UP, Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra. The terminals are Tughlakabad and Dadri in the National Capital Region of Delhi and Jawaharlal Nehru Port (JNPT) of Mumbai.
Communication:The communication network has improved leaps and bounds in the country during last decade. Vodafone, Airtel, BSNL, Reliance communications, Reliance Jio, Aircel, MTS India, Tata India , Indicom Idea, Cellular And Tata Docomo are the service providers in Maharashtra for broadband and voice telephony. Maharashtra has the highest share of the internet market at 18.8%. Most of the industrial areas in Maharashtra have the broadband facilities.
Water: Water is the base of human existence; same is the case with industries. MIDC (Maharashtra Industrial Corporation) meets the requirement of industries with 69 scheme, 5 dams, 7877 HP pump system & 2864 Kms. length pipelines at the nominal cost of Rs. 7 per 1,000 litre water. All industries under MIDC have been provided with piped water unless the water consumption of the industry is too high. Large Industries having high consumption of water are also encouraged in the areas which are close to the source of water. Industries set up in the free hold industrial zone adjacent to MIDC are also provided with piped water by MIDC depending upon the availability.
Power / Electricity: Uninterrupted power supply is the back bone of any industry. The availability of power is quite satisfactory for industries in Maharashtra as compare to other states in India. The power generation portfolio involves thermal, hydel & gas stations along with solar power plant there no power scarcity. Mahagenco (Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Limited) has the highest overall generation capacity and the highest thermal installed capacity amongst all the state power generation utilities in India. Industries in the designated A, B, and C areas—which comprise the core of Maharashtra’s manufacturing, the base tariff for high tension and low tension industrial consumers in these regions is Rs. 8.23 and Rs. 9.31 per unit respectively. MSEDCL provides power connection to the new industries. The power connection to new industries in MIDC area is assured. There is no power cut for the industries situated in MIDC area except for schedule shut down once a week.
Waste Management & Effluent Disposition:The MIDC has made its own arrangements for treatment of effluent. There is no direct or indirect discharge of effluent in the water bodies. Out of 571 effluent generating industries, major units are textile, chemical and bulk drugs, pharmaceuticals, dyes, pesticides etc. The partly treated effluent of the SSI units and fully treated Effluent of MSI/ LSI units is carried through MIDC closed pipe line to Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP). To keep a check on the effluents and the waste produced, MPCB (Maharashtra Pollution Control Board) has laid down various guidelines on the various pollution control norms of the industries. MPCB also issues the consent to establish and operate under various categories i.e. Red, Orange, Green and White. The state of Maharashtra has:-
- 18 operational CETPs and 4 are under construction. Together the capacity of these treatment plants is ~258 MLD.
- The state has 4 CHWTPs at Taloja, TTC, Ranjangaon and Butibori, which is one of the highest in the country. Another 13 CHWTPs have been planned. The aggregate capacity of these plants is 250,000 MT per annum.
- There is 1 operational STP at Hinjewadi with a capacity of 4 MLD, while another 1 is under construction at Waluj of same capacity and 2 more have been planned.
- All the air polluting industries are required to be provided with emission control systems such as Scrubbers, Wet scrubbers, Dust collectors and stacks of sufficient height. MPCB has been monitoring air emission of the industries
- Mumbai Waste Management (MWM) is providing the membership to the industry and collecting solid waste from the industries. Some industries generate hazardous waste from their process. Common Hazardous Waste Treatment Storage and Disposal Facility (CHWTSDF) takes care of the disposal of the Hazardous Waste. The hazardous waste from the industries is discharged at the facility by either direct landfill (DFL) or landfill after treatment (LAT) as required.
Labour:Being India’s second densely populated state, catering world’s best of the university, Head offices of major MNCs are some of the reasons that have resulted in availability of Managerial, skilled and Semi- skilled manpower making it an ideal destination for knowledge based and manufacturing sectors. The unskilled industrial labour is also easily available through the local villages around Industrial Township. The state is one of the most industry-friendly states with one of the lowest labour disputes which is the backbone of industrial sector in Maharashtra. The Government of Maharashtra has fixed the minimum wage for each industrial area.
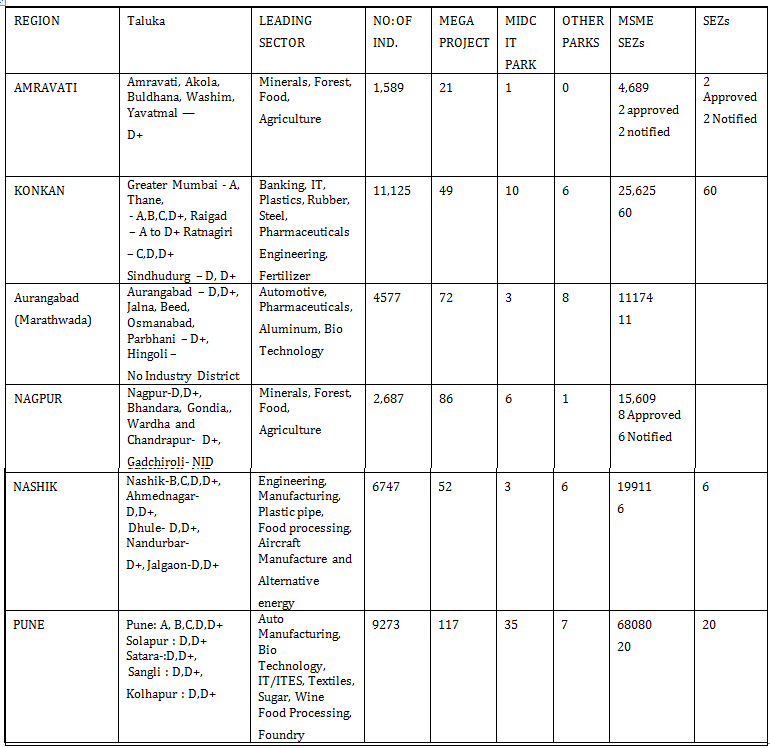
INDUSTRIAL REGIONS & DISTRICTS IN MAHARASHTRA
Progressive Government taking measures to facilitate industries in generating revenue is what the state is working at. Maharashtra Industrial areas are divided into 5 zones A,B,C,D & D+ depending on the advanced Industrial Infrastructure. The list provides Industrial regions & districts (different blocks) in Maharashtra.
- Nashik Region
- Pune Region
- Konkan Region
- Nagpur Region
- Aurangabad Region
- Amravati Region
The Government of Maharashtra has grouped the Districts / cities into 5 Major groups (A to D+) depending upon the development. Two more groups have been added i.e. Areas where there are No Industries and the Areas affected by the Naxalism:-
| Group | District/cities |
| 1. A (Developed areas) | Mumbai, Pune, etc. |
| 2. B (Less developed than A) | Alibagh, Dhanu, Nashik, etc. |
| 3. C (Less Developed than B) | Bhivandi, Ratnagiri, Baramati, etc. |
| 4. D (Less developed than C) | Aurangabad, Satara, Nagpur, etc. |
| 5. D+ ( Less developed than D) | Pithan, Barshi, Kagal, etc. |
| 6. No Industries Exist | Gadchiroli, Hingoli, etc. |
| 7. Areas affected by Naxalism | Gondia, Kinvat, Chandrapur, etc. |
The Package scheme of incentives of Maharashtra provides more incentives to the industries set up under less developed area. To know the details of the package scheme of incentives (PSI) please click
Broad details of industries in various regions are as under:-
CLASSIFICATION OF INDUSTRIAL LAND IN MAHARASHTRA
The Government of Maharashtra has earmarked various industrial zones for setting up the industries. The Government of Maharashtra through Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation (MIDC) acquires the land and gives it on lease for 95 yrs to the Industries. The industries are allowed to be set up on:-





